
| State transition flow control |  |
The readout software manages data acquisition as a simple state machine. The state machine is described in the figure labelled Readout State Machine.
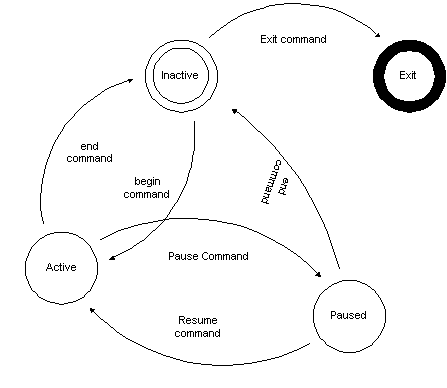
Descriptively:
All state transitions are initiated from outside the trigger thread. For example, command execution will happen either in the Tcl/Tk guest event loop thread, or within one of the TclServer threads. The flow control breaks into two types of transitions. Those that initiate event taking (transitions into the active state), and those that end event taking (transitions into the inactive, or paused state).
Transitions into the Active state will call the CExperiment::Start(). This function will setup and start two threads of control. The clock thread will manage the timing of scaler readouts and keep a run elapsed time for elapsed time fields of the buffer. The trigger thread wil monitor triggers and, on receipt of one, Call CExperiment::ReadEvent() in the context of its thread to read the event.
Transitions out of the Active state will call the CExperiment::Stop() member function. The trigger thread is halted by calling it's stop function. The stop function sets a stop flag in the threads member data and does a Join operation to wait for the thread to actually exit. The clock thread is also halted in the same way. Without an active trigger thread to initiate event readout and a clock thread to initiate periodic scaler readout, the run is effectively halted.
| State transition flow control |  |