Chapter 39. Networked ring buffer access
The NSCL data acquisition system allows data inserted in local ring buffers to be acquired by remote systems. This is done in such a way as to minimize data transfer. The first application to request data from a remote ring contacts the remote system's RingMaster server. The RingMaster runs an instance of ringtostdout on the requested ring, with stdout redirected across the request socket. The local system sets up a proxy ring and starts up an instance of stdintoring with stdin connected to the data transmission socket. Finally the application is connected as a consumer to the proxy ring. Subsequent applications that request data from the same remote ring are simply connected to the proxy ring.
The networked ring buffer access class
CRingAccess provides member functions that make
this operation completely transparent to application code. Ring buffers
are specified using a URI (Universal Resource Identifier), that specifies
the host and remote ring name.
The example above requests data from the ring
mydaq on the host
spdaq22.nscl.msu.edu.
If the host specified is localhost the
CRingAccess will connect the application
directly to the specified local ring without creating a proxy ring.
When attaching to a ring you should construct URIs for rings
as shown below:
Example 39-2. Substituting local host for the hostname in URI's
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
...
string ringUri(string host, string ring)
{
char localHost[100];
char domain[100];
gethostname(localhost, sizeof(localhost));  getdomainname(domain, sizeof(domain));
getdomainname(domain, sizeof(domain));  string fqdn(localHost);
if (host == fqdn) {
host = "localhost";
}
fqdn += domain;
string fqdn(localHost);
if (host == fqdn) {
host = "localhost";
}
fqdn += domain;  if (host == fqdn) {
host = "localhost";
}
string uri("tcp://");
uri += host;
uri += "/";
if (host == fqdn) {
host = "localhost";
}
string uri("tcp://");
uri += host;
uri += "/";  uri += ring;
return uri;
}
uri += ring;
return uri;
}
-
This section of code determines the name of the host.
For spdaq20.nscl.msu.edu e.g., this will
fill
localhostwith localhost 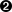
-
This section of code determines DNS domain name of the system.
For spdaq20.nscl.msu.edu
domaingets filled with the string nscl.msu.edu. 
-
This section of code considers the case that
hostis either the unqualified host name (e.g. spdaq20), or the fully qualified host name (e.g. spdaq20.nscl.msu.edu), and if so substitutes localhost to prevent the formation of a proxy ring, when the URI is used to connect to thering 
-
Finally this section of code constructs and returns a string
containing the URI that will specify
ringin the systemhost.
To use the remote access software, you must incorporate the class definitions into your software, tell the compiler how to locate the class header and link your application to the data flow library. The examples below show how to do each of these. The compiler and linker lines assume that you have defined DAQROOT to point to the top level directory of the installed NSCLDAQ.
Example 39-5. Linking code that uses CRingAccess
g++ -o myapp myapp.cpp -L$DAQROOT/lib -lDataFlow -Wl,"-rpath=$DAQROOT/lib"
Remote Ring Access provides reference information about this class library.