2.5. A simple analysis script.
BatchSpecTcl needs to be driven by a script. The script must:
Load the spectcl package.
Load the user's Tcl package that sets up the anlaysis pipeline
Specify the data getter and distributor.
Start Analysis
Save the results.
The sample script below assumes that TCLLIBPATH includes the SpecTcl TclLibs directory and the directory in which your MyPipeline package is stored. We further assume that an interactive SpecTcl has saved its configuration in defs.tcl. This definition file normally contains the spectrum and gate definitions, gate applications and changed tree parameter and tree variable settings.
Example 2-11. Smaple batch SpecTcl script.
package require spectclpackage require MyPipeline
source defs.tcl
filesource run-0003-00.evt
analysissink
puts "analyzing..." analyze
puts "done" set f [open spectra.dat w] foreach spectrum [spectrum -list] { set name [lindex $spectrum 1]
swrite -format ascii $f $name } close $f puts "Spectra written to spectra.dat"
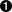
- Requires the SpecTcl batch package. This script requires that TCLLIBPATH includes the TclLibs directory of a SpecTcl installation with version greater than or equal to 5.2-000.
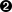
- MyhPipeline is the name of the package created by the Skeleton, unless you change it. This line loads that package which, at initialization, sets up the analysis pipeline that produces parameters from raw events.

- Sources the file that contains the spectrum, gate, gate application definitions and other information that determines what's done with the parameters produced for each event.

- Specifies data will be gotten from file. The file we read will be run-0003-00.evt in the current working directory. This might be a single run event file.

- The main analysis loop will take data read from the getter and distribute them to the SpecTcl analysis subsystem.

- Analyzes the entire file.

- This chunk of code opens the file specta.dat, loops over all spectrum definitions and writes the spectra that have been accumulated to that file. Using interactive SpecTcl you can read this file using a similar loop:
The catch command is used because att the end of the file, there may be an empty line which won't let the end file condition be discovered until after an attempt is made to read a spectrum that is not there.
Example 2-12. Reading a file with several spectra:
set f [open spectra.dat r]
while {![eof $f]} {
catch {sread -format ascii -nosnapshot -replace $f}
}
close $f
You can certainly modify the analysis so that it analyzes more than one file or even more than one run. Suppose the current directory contains several runs and the order in which the file segments whithin each run is processed is unimportant. To analyze all segments of runs 1 through 10, the following could be done (after the packages and definitions have been loaded):
Example 2-13. Reading several multi segmented runs:
...
analysissink
for {set run 1} {$run <= 10} {incr run} {
clear -all
set namePattern [format run-%04d-*.evt $run]
set files [glob $namePattern]
puts "Analyzing run $run"
foreach file $files {
filesource $file
analyze
puts "Analyzed segment $file"
}
puts done
set f [open run-$run.spec]
for spectrum [spectcrum -list] {
set name [lindex $spectrum 1]
swrite -format ascii $name $f
}
close $f
puts "Wrote spectra to run-$run.spec"
}
By now this script should be understandable. Note how prior to analyzing the event files for each run, the spectra are cleared. Note as well that spectra for each run are written in a file that has the run number it its name.
Note that the segments in a run will be analyzed out of order. Furthermore a simple set files [lsort [glob $namePattern]] will only work if there are less than 100 segments in the run as the file run-0001-100.evt sorts alphabetically prior to run-0001-002.evt
Here's a Tcl fragment that provides a proc that sorts the list of run segments for a run in segment order.
Example 2-14. Ordering run segments by segment number
proc compare {file1 file2} {
scan $file1 run-%04d-%02d.evt run seg1
scan $file2 run-%04d-%02d.evt run seg2
if {$seg1 < $seg2} {return -1}
if {$seg1 > $seg2} {return 1}
return 0
}
proc sortRun {filelist} {
return [lsort -increasing -command compare $filelist]
}
This uses the ability of the lsort command to accept a command that defines the collation order of the list it's sorting.